Option Combos
The functions below can be used for
handling combinations of options, such as Spreads, Straddles,
Strangles, Condors, Butterflies, etc. Option combos are mainly used for limiting
risk. For an introduction to options trading, see
Financial Hacker.
The image below shows the profit or loss of an Iron Condor combo dependent of
the underlying price, at expiration (blue) and halfway to expiration (red).
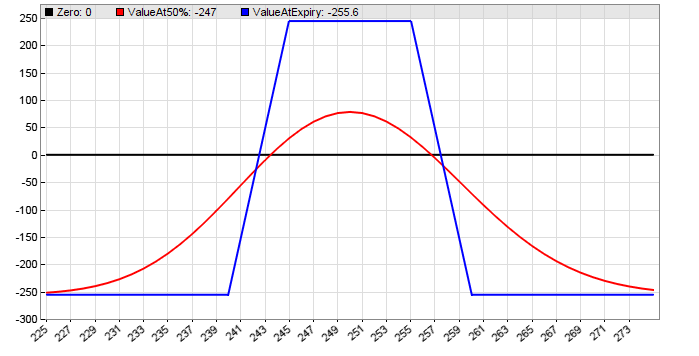
Iron Condor payoff
diagram (Payoff.c)
combo (CONTRACT* C1, int N1, CONTRACT* C2, int N2, CONTRACT* C3, int N3,
CONTRACT* C4, int N4): int
Combines 2, 3, or 4 option contracts C1..C4 to a combo. The number
and trade direction of contracts are given by N1..N4; use negative
numbers for selling and positive numbers for buying, f.i.
-2 for short selling two contracts. C3/N3
and C4/N4
can be 0 for combos with only 2 or 3 legs. Returns the number of combo legs, i.e. the number of different contracts of the
combo. If all numbers N are 0, or if any CONTRACT* pointer is zero while
its associated
number N is nonzero, the combo is disabled and the function returns
0. Source code in contract.c.
comboAdd (CONTRACT* C, int N): int
Adds a copy of the option contract C to the current combo. Amount
and trade direction of the contract is given by N; use a negative
number for selling and a positive number for buying. Returns the number of
the current combo leg. If C is 0, the function deletes all contracts from
the combo and returns 0.comboLegs (): int
Returns the number of legs of the current combo that was defined before with
combo() or comboAdd() calls.
comboContract (int Leg): CONTRACT*
Pointer to the CONTRACT struct of the combo leg with the given
number (1..4). Macro defined in contract.c.
comboLeg (int Leg): int
Selects the contract of the combo leg with the given number (1..4), and returns
the number assigned to that contract as defined in the
combo() function. The number is negative for selling and positive for
buying, so it can be directly used for the Lots parameter
passed to enterLong.
comboStrike (int Leg): var
Returns the strike value of the given combo Leg (1..4).
Source code in contract.c.
comboProfit (var Price, int Sign): var
Returns the profit or loss of the current bought (Sign == 1) or
sold (Sign == -1) combo when expiring at the given Price.
Type, fAsk, and fBid of all contracts of the combo must be set, so
contractPrice should have been called before; the other contract
parameters don't matter. Multiplier and transaction costs are not included. Source code in contract.c.
comboRisk (int Sign): var
Returns the maximum possible loss of the current bought (Sign == 1) or
sold (Sign == -1) combo. For combos with unlimited loss,
returns the loss when the price drops to zero or ends up at twice the strike,
whichever is worse. Type, fAsk, fBid,
and fStrike of all contracts of the combo must be set, so
contractPrice must have been called before; the other contract
parameters don't matter. Multiplier and transaction costs are not included. Source code in contract.c.
comboPremium (int
Sign): var
Returns the premium of the current bought (Sign == 1) or
sold (Sign == -1) combo, also referred to as the combo's ask
and bid price. Positive premium is earned, negative
premium is paid. If the combo consists of long and short positions, its ask
price can be lower than its bid price. fAsk and fBid of all
contracts of the combo must be set, so contractPrice
should have been called before; the other contract parameters don't matter. Multiplier
and Transaction costs are not included. Source code in contract.c.comboType ():
int
Returns the combo type: 1 for a single put, 2
for a single call, 6 for a call spread, 7 for a strangle (call and put),
8 for
a put spread, 13
for a call butterfly (3 calls), 14 for a put butterfly (3 puts),
and
20 for a 4-contract combo such as a condor (2 calls and 2 puts). Source code in contract.c.comboMargin (int
Sign, int AssetType): var
Calculates the margin cost of the current bought (Sign == 1) or
sold (Sign == -1) combo with the given AssetType.
Uses the margin formula on the Interactive Broker's
US Options Margin Requirements page. Supports single calls and puts, call
spread, put spread, strangle (call and put), Butterfly with 3 calls, Butterfly
with 3 puts, and Condor (2 calls and 2 puts). Source code in
contract.c.
Parameters:
| C1..C4 |
CONTRACT* pointer for leg 1..4, or 0 when the leg is not used
in the combo. |
| N1..N4 |
Number of contracts for leg 1..4, negative for selling and positive for
buying contracts. 0 when the leg is not used in the combo. |
| Leg |
Number of the combo leg, 1..4, starting with 1
for the first contract. |
| Sign |
Position sign, -1 for short and 1 for
long. |
| AssetType |
1 for a currency, 2 for an index,
3 for stocks and ETFs. The margin for futures must be
individually calculated. |
comboPrint (int To)
Prints the parameters of the current combo contracts to the destination
To, as in print(To,...).
plotCombo (var HistVol, var Min, var Max, int Days, int
Modus)
Plots the payoff diagram of the current combo
with volatility HistVol from price Min to
price Max. Modus 0 initializes the plot and
plots a zero line, Modus 1 plots the diagram at expiration,
Modus 2 at the given Days into the lifetime (R
and RQuantLib
required), and Modus 3 plots the Delta. Type, strike, ask, bid,
and expiry in days must be set in all contracts of the combo. Two different
expiration periods are supported. Source code in contract.c;
usage example in PayOff.c.
Remarks:
- contract.c must be included for all above functions.
- Combo trades should be opened or closed in the order of legs, starting
with leg 1. They are then automatically combined to a combo order which is sent to the broker
with the last leg.
Many brokers offer reduced margin and commission on combos. The combo order
internally uses the SET_COMBO_LEG command,
which must be supported by the broker plugin. Otherwise the combo is split
in separate contract orders. Make sure that all legs of the combo are
entered together; "pending
legs" won't work.
- Order limits are normally interpreted by the
broker as a price limit of the whole combo. The Stop
variable affects individual legs; closing the whole combo at a certain loss
must be handled by script.
- Combos orders can take several minutes for being executed, even at
market. For this reason it is recommended to use GTC
orders and/or to increase the wait time with the
SET_WAIT command.
- If a combo order is not opened by the broker, the
enter call with the last leg will fail. In that case cancel the
preceding legs with the cancelTrade function.
- The elements of the current combo can be accessed through the
ThisCombo pointer, defined in trading.h.
- The current combo remains valid until the next combo()
or contractUpdate() call.
- Use the algo function for getting separate
combo-specific statistics. For determining the current profit/loss of a
combo position, use a trade loop and sum up all
TradeProfit of the same
TradeAlgo. Trades of the same combo are listed in sequence in the trade
loop.
- The script Payoff.c contains definitions of
often used combos, such as spread,
strangle, butterfly,
condor. You can
enter an individual combo for plotting its profit/loss curve.
- For brokers with a different combo margin structure, the
comboMargin function can be copied from contract.c
into the strategy script and accordingly modified.
Example (see also Workshop 8 and Payoff.c):
if(combo(
contract(CALL,Days,Strike),1,
contract(PUT,Days,Strike),1,
0,0,0,0)) // Strangle combo
{
enterLong(comboLeg(1));
enterLong(comboLeg(2));
}
See also:
contract, contract variables,
Workshop 8
► latest version online

